What will this winter have in store for Thornton? Forecasters at the Climate Prediction Center have released their outlook and for the Front Range, it doesn’t hold much in the way of clues.
The CPC does show odds favor above average temperatures for much of Colorado for the period from December through February. In terms of precipitation, the agency gives equal chances of near average, well above average, or well below average precipitation for most of the state. The one exception is the southern third of Colorado which they peg at having above average chances of a drier than normal year.
From NOAA:
U.S. Winter Outlook predicts warmer, drier South and cooler, wetter North
Drought expected to persist in California and expand in the Southeast
October 20, 2016 – Forecasters at NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center issued the U.S. Winter Outlook today, saying that La Nina is expected to influence winter conditions this year. The Climate Prediction Center issued a La Nina watch this month, predicting the climate phenomenon is likely to develop in late fall or early winter. La Nina favors drier, warmer winters in the southern U.S and wetter, cooler conditions in the northern U.S. If La Nina conditions materialize, forecasters say it should be weak and potentially short-lived.
“This climate outlook provides the most likely outcome for the upcoming winter season, but it also provides the public with a good reminder that winter is just up ahead and it’s a good time to prepare for typical winter hazards, such as extreme cold and snowstorms,” said Mike Halpert, deputy director, NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center. “Regardless of the outlook, there is always some chance for extreme winter weather, so prepare now for what might come later this winter.”
Other factors that often play a role in the winter weather include theArctic Oscillation, which influences the number of arctic air masses that penetrate into the South and create nor’easters on the East Coast, and the Madden-Julian Oscillation, which can affect the number of heavy rain events in the Pacific Northwest.
The 2016 U.S. Winter Outlook (December through February):
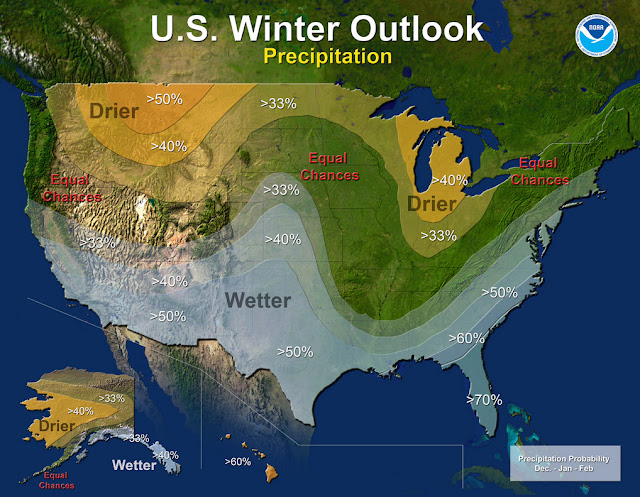
Precipitation
- Wetter than normal conditions are most likely in the northern Rockies, around the Great Lakes, in Hawaii and in western Alaska
- Drier than normal conditions are most likely across the entire southern U.S. and southern Alaska.
Temperature
- Warmer than normal conditions are most likely across the southern U.S., extending northward through the central Rockies, in Hawaii, in western and northern Alaska and in northern New England.
- Cooler conditions are most likely across the northern tier from Montana to western Michigan.
- The rest of the country falls into the “equal chance” category, meaning that there is not a strong enough climate signal in these areas to shift the odds, so they have an equal chance for above-, near-, or below-normal temperatures and/or precipitation.
Drought
- Drought will likely persist through the winter in many regions currently experiencing drought, including much of California and the Southwest
- Drought is expected to persist and spread in the southeastern U.S. and develop in the southern Plains.
- New England will see a mixed bag, with improvement in the western parts and persistence to the east.
- Drought improvement is anticipated in northern California, the northern Rockies, the northern Plains and parts of the Ohio Valley.
This seasonal outlook does not project where and when snowstorms may hit or provide total seasonal snowfall accumulations. Snow forecasts are dependent upon the strength and track of winter storms, which are generally not predictable more than a week in advance. However, La Nina winters tend to favor above average snowfall around the Great Lakes and in the northern Rockies and below average snowfall in the mid-Atlantic.
NOAA produces seasonal outlooks to help communities prepare for what’s likely to come in the next few months and minimize weather’s impacts on lives and livelihoods. Empowering people with actionable forecasts and winter weather tips is key to NOAA’s effort to build aWeather-Ready Nation.